Are Heat Pumps Worthwhile for Texas Summers and Winters?
You’ve heard of heat pumps, maybe your neighbors even have one installed. But are they worth the expense – and what real benefit do they bring to Texans looking for relief from the blistering summer heat and occasional winter freezes? In this article, we’ll break down what makes them efficient for both heating and cooling, as well as key questions homeowners should ask before making the switch.
How Heat Pumps Work
Heat pumps work by transferring heat from one place to another, rather than generating heat. In the summer, they extract heat from inside your house and blow it outside – and they often use less energy than air conditioning units, because of their efficiency. In the winter, they flip this process by drawing heat from the outside air (even in cold temperatures) and bringing it inside to warm your home.
Generally speaking, heat pumps are great performers in the Texas climate. Unlike in very cold regions of the country, where heat pumps may struggle to find enough ambient heat in freezing conditions, most parts of Texas experience relatively mild winters, making heat pumps an excellent year-round solution.
Are Heat Pumps Effective During Summer Heat Waves and Winter Cold Snaps?
The Lone Star State is well-known for extreme summer heat waves, and residents in northern parts of the state, such as Dallas-Fort Worth, are familiar with occasional winter freezes. Modern heat pumps are designed to handle such extremes. That said, in the most extreme heat or cold, a heat pump's efficiency might decrease. Since Texas doesn't typically experience long periods of freezing temperatures, for most homes, a heat pump will handle even cold snaps without a problem. For residents in areas that experience regular below-freezing winters (like parts of the Texas Panhandle), a dual-fuel system that incorporates a backup heat source such as a furnace can be a smart option.
Pros and Cons of Heat Pumps
Pros:
Heat pumps are highly energy efficient, because they transfer heat rather than generate it. For Texas homeowners, this translates to potentially lower utility bills, especially in milder winters.
Heat pumps can both heat and cool, replacing the need for separate heating and air conditioning units.
Because heat pumps use less energy than traditional heating and cooling systems, they produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions.
Heat pumps offer even heating and cooling without the temperature fluctuations that can occur with traditional systems.
Cons:
Heat pumps may have a higher upfront installation cost compared to conventional HVAC systems.
While effective in most of Texas, heat pumps can lose some efficiency during extended periods of extreme cold, though this is rarely a concern for much of the state.
How Do Heat Pumps Affect Electricity Usage?
Because heat pumps rely on electricity, they can increase your overall electric consumption, especially during colder months when the system has to work harder to extract heat. However, compared to traditional electric heating systems, heat pumps are much more efficient, often using up to 50% less energy. If the price you pay for electricity fluctuates based on demand (a variable rate plan), the efficient use of electricity by a heat pump can help reduce costs, particularly if you optimize usage with energy-saving strategies like using a programmable or smart thermostat.
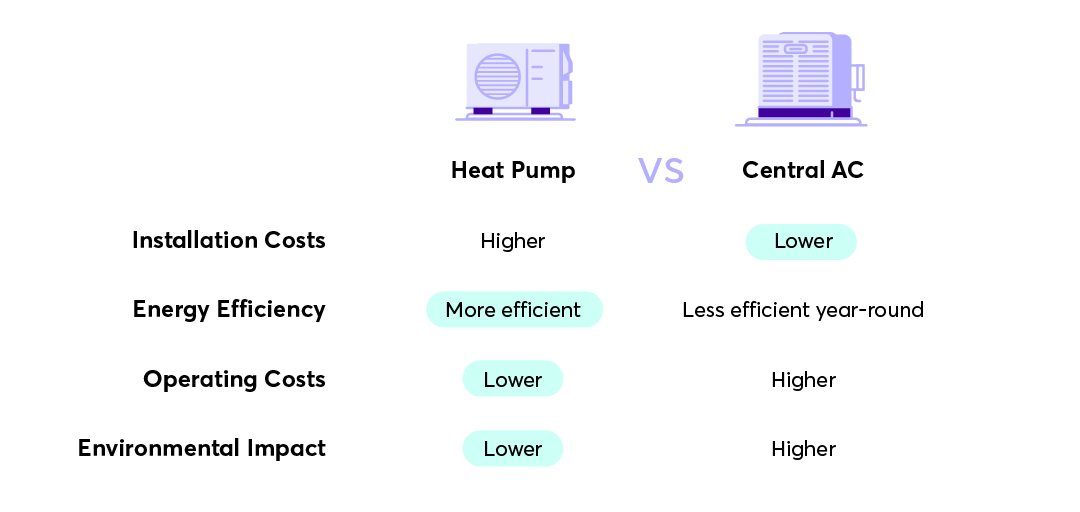
Cost Comparison: Heat Pumps vs. Traditional Systems
While the initial cost of purchasing and installing a heat pump can be higher than that of traditional HVAC systems, the long-term savings can make it worthwhile.
Energy Savings
Heat pumps can reduce your heating costs by up to 50% compared to electric resistance heating (such as baseboard heaters or space heaters) and by around 20-30% compared to gas furnaces.
Cooling Costs
In cooling mode, heat pumps are on par with high-efficiency air conditioners, often operating more efficiently in milder temperatures.
Over time, these savings can add up, especially with energy costs being on the rise. On average, homeowners in Texas can recoup their initial investment in a heat pump within 5-10 years.
How to Size a Heat Pump for Your Texas Home
Determining the right size and capacity for a heat pump is key for optimizing performance. A unit that’s too small won’t adequately heat or cool your home, while one that’s too large will cycle on and off too frequently, wasting energy.
To size a heat pump, take into consideration your home’s square footage, insulation quality, and window orientation, as well as the local climate. To make sure you get the right size for your home, it’s best to consult with a professional HVAC contractor who understands the region's demands, asking them to conduct a "Manual J" load calculation, which takes into account all these factors.
Maintenance Requirements for Heat Pumps
Like any HVAC system, heat pumps require regular maintenance to run efficiently. Common maintenance tasks include:
Change dirty filters, which reduce airflow and force the system to work harder, increasing energy use.
The outdoor unit's coils can accumulate dirt and debris, reducing efficiency. Cleaning these coils ensures proper heat exchange, so be sure to clean them regularly.
Check refrigerant levels, which are critical for efficient operation in both heating and cooling modes.
A yearly check-up from a certified technician will help you catch any potential issues before they become costly problems.
Lifespan of Heat Pumps in Texas
On average, a well-maintained heat pump can last between 10 to 15 years in Texas, depending on usage and environmental factors. The milder winters in most parts of Texas reduce strain on the system, which can contribute to a longer lifespan compared to colder climates.
Smart Home Integration with Heat Pumps
Advancements in smart home technology make it easier than ever to get the most out of heat pumps – keeping your home comfortable while maximizing energy efficiency. Smart thermostats can be linked to heat pumps to allow for precise temperature control, remote monitoring, and energy-saving settings like scheduling when your system turns on and off.
Environmental Benefits of Heat Pumps
Heat pumps are a greener alternative to traditional heating and cooling systems. Unlike gas furnaces, they don’t rely on burning fossil fuels, and so create fewer greenhouse gas emissions. This is particularly relevant in Texas, where reducing energy consumption during peak demand times (like during summer heatwaves) can alleviate stress on the grid and reduce the need for carbon-intensive power plants.
Pairing Heat Pumps with Renewable Energy Sources
Even better? Combining heat pumps with renewable energy sources like solar panels – after all, Texas has so much glorious sunshine! By using solar power to run a heat pump, you can drastically reduce or even eliminate your electricity bill, while significantly cutting your home’s carbon footprint.
Incentives and Rebates for Installing Heat Pumps in Texas
In Texas, state and private institutions offer rebates and incentives for energy-efficient home improvements, including heat pumps. These programs may be offered by local utility companies, state agencies, or federal initiatives like the Residential Renewable Energy Tax Credit, which provides a tax break for energy-efficient upgrades.
Utility companies such as Oncor and CenterPoint have historically offered rebates for homeowners who upgrade to energy-efficient HVAC systems, including heat pumps. It’s always a good idea to check with your local utility provider to see what incentives are available.
Heat Pump Benefits by Region
Because Texas is so spread out, with a wide range of climates from the humid Gulf Coast to the dry plains of West Texas, the performance of heat pumps can vary based on local conditions:
Coastal Areas (e.g., Houston, Corpus Christi)
Coastal regions experience high humidity and warmer temperatures year-round. Heat pumps perform well in these areas, especially in cooling mode, where their dehumidifying capabilities are a bonus. Heat pumps designed for humid climates can help reduce indoor moisture, improving overall comfort.
Inland and Northern Areas (e.g., Dallas, Lubbock)
These regions experience more distinct seasons, with hot summers and colder winters than other parts of the state. Heat pumps are effective here too, but homeowners may want to consider models that are rated for colder temperatures, or pair a heat pump with a secondary heating source (like a furnace) for backup during rare cold snaps.
West Texas (e.g., El Paso, Midland/Odessa)
In the dry, desert-like climate of cities like Midland and Odessa in West Texas, heat pumps excel due to their efficiency in transferring heat. The relatively mild winters in these areas make heat pumps an excellent choice year-round.
FAQ
What are the benefits of heat pumps?
Heat pumps offer a highly efficient, versatile solution for Texas homeowners looking to save on energy costs while reducing their carbon footprint.
What regions of Texas are best for heat pumps?
Whether you're in a humid coastal area or a dry inland region, there’s likely a heat pump model that suits your needs. If you live in a part of the state that experiences colder winters, be sure to find a model that is rated for cold climates.
Can heat pumps work alongside advances in technology and renewable energy?
By pairing a heat pump with smart home technology – and even renewable energy sources like solar panels – you can potentially reduce your energy bills and carbon footprint even more!




