Air Conditioning Unit or Heat Pump: Which Is Best for Texans?
Faced with a choice between a heat pump or an air conditioning unit? Whether you live in the heat of Houston or cooler climates of West Texas, you know that you want a system that can stand up to simmering summers as well as freezing cold winters… So which will work best? We’ve put together a comparison of the two, based on energy efficiency, cost, maintenance, performance, and more, to help you buy smart.
Pros and Cons of AC Systems vs. Heat Pumps
AC System Pros and Cons
Air conditioning units are highly effective at cooling, especially in Texas' long and hot summers. They can be cheaper to install and have been around for years, so accessing professional maintenance and repair services is easy.
On the down side, they only cool the air, so an additional heating system is needed for colder months, they can be less energy-efficient compared to modern heat pumps, and typically have higher operational costs.
Heat Pumps Pros and Cons
The pros of heat pumps start with the fact that they offer both heating and cooling, which makes them versatile year-round. They are also energy efficient, especially in areas with moderate climates, cost less to operate in temperate seasons, and have a lower carbon footprint.
On the cons side, they can be less effective in extreme heat or cold without supplemental systems, initial installation cost can be higher, and some systems struggle in climates that experience very cold winters.
Are Heat Pumps or AC Units More Energy-Efficient for Texas’ Climate?
Here in Texas, we have a wide variety of climates, from the sweltering summers in Central and Southern Texas to the cooler conditions in the Panhandle. Heat pumps tend to outperform traditional AC systems in energy efficiency, especially in regions with moderate winters. A heat pump can operate efficiently at outdoor temperatures as low as 25°F to 30°F – so in many parts of Texas, the dual heating and cooling function makes heat pumps more energy-efficient. Air conditioners, while they are highly efficient at cooling, tend to consume more energy over time in hot climates, especially when combined with separate heating systems in winter.
Costs of AC Units vs. Heat Pumps
Installation Costs
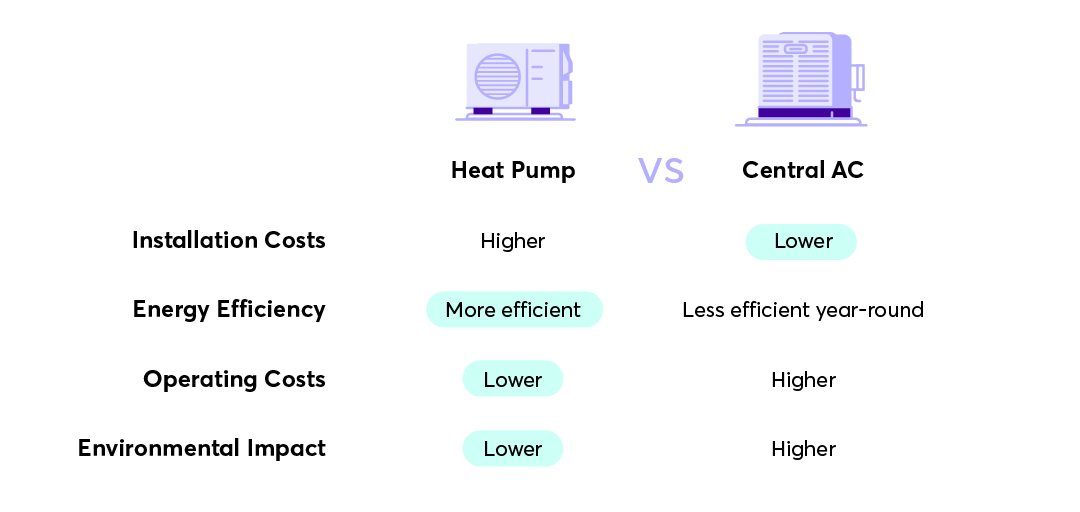
Heat pumps have higher initial installation costs, especially if you’re installing a dual system that handles both heating and cooling. The installation of a heat pump can range from $4,000 to $10,000 depending on the system type, size, and complexity. Traditional AC systems, depending on the unit size and SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio), can range from $3,000 to $7,000 for installation. If you already have a heating system in your home, the initial AC investment may be lower.
Operating Costs
Heat pumps generally use less electricity over the course of a year than AC systems. In winter, their efficiency can drastically lower heating costs compared to electric resistance heating or gas furnaces. Over time, the savings in utility bills can offset the higher upfront cost. Air conditioners are less efficient overall, particularly in energy use during Texas’ long hot months, leading to higher electricity bills.
Maintenance Costs
Heat pumps require more frequent maintenance checks, because they run all year long – costs average around $150 to $300 annually. However, newer models are built for durability, and regular servicing will keep them efficient.. AC units, since they are used mainly in summer, have less wear and tear over the year, so maintenance is typically cheaper, around $100 to $200 per year.
Rebates and Incentives
Homeowners considering a heat pump can find a range of rebates and federal incentives, especially as heat pumps help out with energy-efficient and renewable energy initiatives. The federal government offers tax credits up to 30% for installing heat pumps under the Inflation Reduction Act. Some Texas utility companies also offer rebates for energy-efficient HVAC installations, including heat pumps. AC systems are generally not as incentivized as heat pumps, but may still qualify for certain rebates or incentives if they meet energy efficiency standards such as ENERGYSTAR® ratings.
Performance Comparison of AC Units vs. Heat Pumps
Energy Efficiency
Heat pumps are overall more energy-efficient, particularly for heating. Air-source heat pumps can achieve up to 300% efficiency by moving heat instead of generating it! While AC systems are improving in SEER ratings, they generally max out at around 20-25 SEER, making them less efficient than heat pumps for year-round performance.
Heat pumps perform best in climates with moderate winter temperatures, making them well-suited for most parts of Texas. However, in areas with long stretches of extremely hot weather, like South Texas, they may not cool as efficiently as AC units.
For smaller homes, particularly in milder areas of Texas, a heat pump can efficiently handle both heating and cooling needs. Larger homes or those located in extremely hot regions may benefit from the more robust cooling power of an AC unit paired with a traditional furnace.
Comfort and Temp Control
Both systems provide good temperature control, but heat pumps are better at maintaining steady temperatures all year long. High-efficiency heat pumps also come with variable speed options, which improve comfort levels by reducing temperature swings. And when it comes to noise levels, AC systems are typically louder during operation (especially the compressor units) while heat pumps tend to be quieter, especially in mild weather when they don't need to work as hard.
Smart Home Integration
Both heat pumps and AC systems can integrate with smart thermostats and home automation systems like Google Nest and Amazon Alexa, giving you a lot of control over the temperature, as well as letting you monitor their efficiency.
Maintenance and Durability of AC Units vs. Heat Pumps
Both types of systems require regular maintenance, but heat pumps, as they are used year-round, may need more frequent service checks. However, newer models are quite durable with regular upkeep. AC systems, used mainly in summer, may have lower maintenance costs but still require annual servicing to maintain efficiency.
Heat pumps generally last around 15-20 years, depending on usage and maintenance. AC systems have a similar lifespan, around 12-20 years, though excessive use during Texas summers may knock a few years off of this timeline.
Environmental Impact of AC Units vs. Heat Pumps
Heat pumps offer a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to AC systems, especially when powered by renewable electricity sources. Since they move heat rather than generate it, they require less energy. AC units, while they are becoming more and more energy-efficient, still rely heavily on electricity – and if your power is generated from fossil fuels, this can lead to higher greenhouse gas emissions.
Impact on the Texas Grid
Heat pumps, especially when powered by renewable energy, significantly reduce carbon emissions compared to traditional AC systems. Texas’ energy grid is heavily reliant on fossil fuels, but heat pumps provide a more efficient use of electricity, reducing the demand on the grid. As Texas shifts more towards renewable energy, heat pumps could become an even more environmentally friendly option. AC systems, while improving in efficiency, place a heavier load on the grid during peak summer months, often requiring fossil-fuel-generated electricity to power them.
Use of AC Units vs. Heat Pumps in Urban vs. Rural Settings
In cities, heat pumps offer a more energy-efficient and versatile solution for both heating and cooling. Infrastructure in urban areas supports efficient energy use, making heat pumps a smart choice for year-round comfort. In rural areas, particularly where electricity costs may be higher or less reliable, traditional AC systems paired with a gas furnace may be a more practical option. Heat pumps in these regions can still be effective but often require backup systems.
FAQ
Is investing in a heat pump worth it in Texas?
Yes, particularly if you live in a region with moderate winters and are concerned about long-term energy savings and environmental impact.
How effective are heat pumps during extreme Texas summers?
Modern heat pumps are highly effective, though in areas with extreme heat, a traditional AC may cool more rapidly.
How reliable are heat pumps in areas with frequent power outages or grid instability?
In areas with frequent power outages or grid instability, the reliability of heat pumps can be a concern, because they rely entirely on electricity to operate – and so will stop working during a power outage, meaning that no heating or cooling is available until power is restored. So many homeowners in areas with frequent outages opt for backup power sources such as generators or solar panels with battery storage, which allow the heat pump to continue functioning even during an outage.